The Indian securities market is rapidly transforming through digital technologies and Artificial Intelligence (AI). This shift is revolutionising investment strategies, risk management, and regulatory oversight, moving from traditional methods to more automated systems. The Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) leads this change, actively pursuing digitalisation and innovation to remain competitive.
Here's an in-depth look at the future of Indian stock exchanges, focusing on BSE's strategic approach to digitalisation and innovation.
Table of Contents
- The Digital Transformation of Indian Capital Markets
- Artificial Intelligence's Impact on the Indian Securities Market
- BSE's Strategic Response to Digitalisation
- Regulatory and Ethical Considerations for AI
- Future Outlook and Recommendations for BSE
- Conclusion
- FAQs: Indian Stock Exchanges & Digitalisation
The Indian capital market is increasingly integrating AI and digital technologies. This revolution reshapes investment, decision-making, and strategy, making technology a strategic asset for risk management and regulatory oversight.
The National Stock Exchange of India (NSE) is globally recognised for its advanced technology. Similarly, the BSE embraces significant digital transformations, marking a structural shift in financial market navigation. This comprehensive digital push is modernising the entire financial ecosystem.
From Manual to Electronic Trading
Historically, Indian stock trading was a manual, paperwork-heavy process, with brokers physically present at exchanges. The BSE, founded in 1875, initially operated under a banyan tree on Dalal Street.
However, AI-driven trading systems have led to a paradigm shift, featuring algorithmic trading, data-driven decisions, and high-speed transactions. The BSE transitioned to its electronic BOLT platform in 1995, and NSE introduced its Automated Electronic Exchange Trading System in 1992. This rapid transition underscored India's commitment to modernising its financial infrastructure.
Key Drivers of Digitalisation in India
India's financial landscape is transforming, with millions of new investors entering the market via digital platforms. This growth necessitates a paperless trading system, driven by several key factors.
- Rising Retail Participation: More Indians invest directly in stocks and funds. Digital platforms democratise investing, making tools accessible, with over 45% of trades via mobile apps.
- Regulatory Push: SEBI promotes investor protection and transparency through digitalisation. New rules oversee algorithmic trading, and a unified compliance reporting platform is set for 2025.
- Need for Speed: Modern trading demands same-day settlements. India has moved to T+1 and aims for T+0, eventually targeting instant settlement.
- Government Vision: The "Digital India" movement builds a robust online infrastructure, fostering a more interconnected and efficient financial ecosystem.
These drivers propel India's financial market towards a fully digital future, enhancing accessibility, transparency, and efficiency. The concerted efforts from government, regulators, and market participants are paving the way for a truly digital economy.
The Pivotal Role of Depositories (NSDL & CDSL)
India's digital shareholding system relies on two main depositories: National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL) and Central Depository Services Limited (CDSL). These organisations are the backbone of electronic trading.
They eliminate risks like theft or forgery associated with physical share certificates. SEBI and the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) mandate dematerialisation for share transfers. Investors use demat accounts with Depository Participants (DPs) for seamless trading and real-time portfolio monitoring. These depositories are fundamental to ensuring the integrity and efficiency of the digital trading environment.
Wrap-up: Indian capital markets have undergone a sweeping digital transformation, shifting from manual processes to AI-powered, high-speed trading systems. This evolution, backed by regulatory support and growing retail participation, is driving India toward a fully digital financial ecosystem.
Want to analyse BSE’s recent stock movement, updated chart patterns, and key valuation metrics? Check the BSE share price now to evaluate its current market performance.
AI integration in India's capital market profoundly revolutionises investment strategies and decision-making. AI software can scan vast data, identify patterns, and execute trades independently, a domain once exclusive to human minds.
This transformation empowers both retail and institutional investors. AI helps them detect market trends, predict movements, and optimise asset allocation with unprecedented precision. This shift enhances speed, efficiency, and accuracy, setting new standards for market performance.
AI Applications and Technologies
AI software now scans data, identifies patterns, and executes trades independently, enhancing financial operations' speed, efficiency, and accuracy. The AI revolution in finance is driven by:
- Machine Learning (ML): Used in trading algorithms to predict market movements and optimise decisions from vast datasets.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Processes text from news and social media for sentiment analysis, gauging investor mood and anticipating market reactions.
- Big Data Analytics: Processes huge volumes of data for actionable insights, vital for robust trading strategies and effective risk management.
AI techniques revolutionise investment strategies. Robo-advisors manage portfolios. AI programs execute trades based on rules and conditions. AI models analyse data to forecast stock prices and evaluate qualitative information. Real-time fraud detection systems also use AI to identify systemic risks. These technologies collectively enable a more intelligent, responsive, and efficient financial market.
Benefits of AI in Trading
The integration of AI in stock trading offers significant advantages, enhancing market efficiency and investor confidence.
Key AI Applications and Benefits
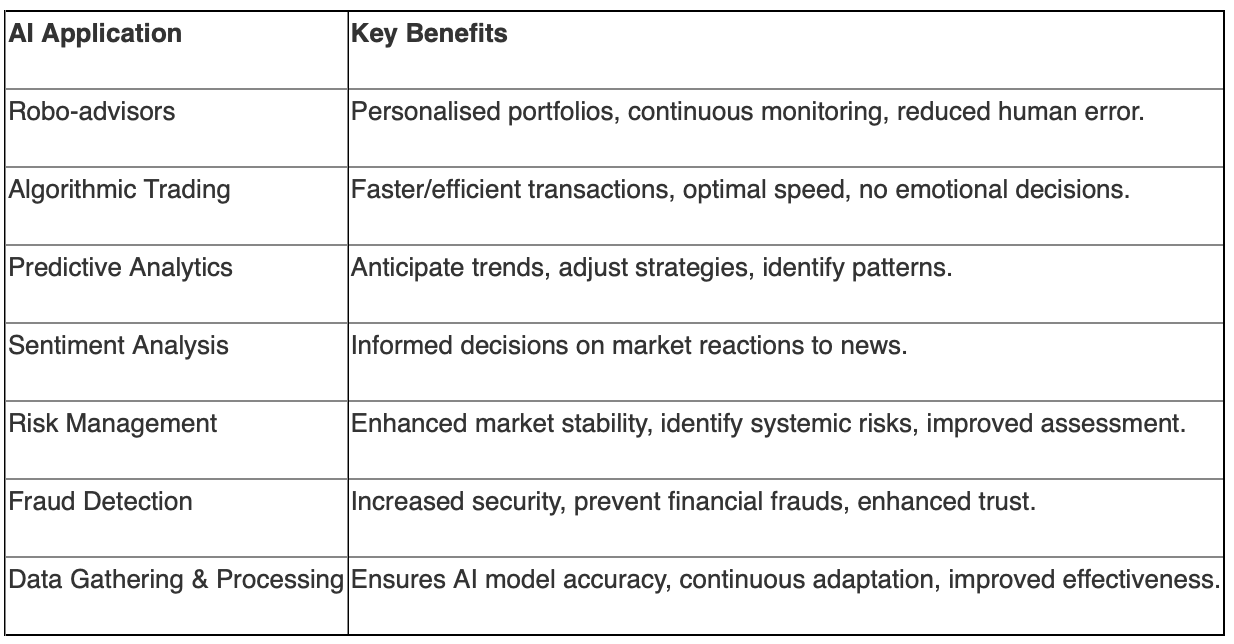
These benefits collectively contribute to a more dynamic and effective trading environment, supporting both institutional and retail investors.
Challenges and Risks of AI in Trading
Despite its advantages, AI-driven trading introduces risks that require careful management.
- Market Stability: AI systems can amplify price swings, potentially leading to flash crashes. Widespread AI adoption with similar trading patterns may cause systemic instability.
- Regulatory & Ethical Concerns: India lacks specific AI regulations for securities trading. Auditing opaque "black box" AI decisions is difficult, raising concerns about fairness and algorithmic bias.
- Operational & User Risks: AI platforms collect vast data, raising cybersecurity risks. Over-reliance on AI without human oversight can lead to misjudgments during unpredictable events.
These challenges necessitate robust regulatory frameworks, ethical guidelines, and continuous monitoring to ensure market integrity and investor protection. Addressing these concerns is crucial for sustainable AI integration.
Wrap-up: Artificial Intelligence is reshaping India's securities market by enhancing trading precision, speed, and investor access. However, its widespread adoption also introduces systemic risks, regulatory challenges, and ethical concerns that demand balanced oversight.
The Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) is a key player in India's financial market digitalisation. Its strategic response involves continuous technological upgrades and adaptive market strategies to maintain its competitive edge.
The BSE's journey demonstrates a proactive approach to embracing technological advancements. This ensures it remains a modern, efficient, and secure platform for investors, actively shaping the future of Indian capital markets.
Digital Evolution and Strategic Investments
BSE transitioned to electronic trading in 1995 with its BOLT system and supported smartphone trading by 2010. Recognising robust digital infrastructure, CtrlS Datacenters partnered with BSE to enhance its data centre, crucial for maintaining market integrity and secure access for its investors.
BSE Ltd's revenues reached 3,212 crore in 2025. The exchange plans to invest more and deepen supplier relationships for its Digital and IT transformation projects. Research indicates BSE Ltd will invest in emerging technologies like AI, Machine Learning (ML), IoT, Blockchain, and Autonomous Database. This demonstrates BSE's commitment to continuous technological enhancement, ensuring it remains at the forefront of financial innovation and operational excellence.
Competition in the Derivatives Market
Competition between NSE and BSE, particularly in options, has intensified. NSE long dominated India's derivatives market, but BSE made strides due to SEBI's push for a level playing field.
BSE's Derivatives Market Share
|
Timeframe
|
Market Share
|
|
FY23
|
Less than 1%
|
|
FY25 (Current)
|
26%
|
BSE's share increased due to rising Sensex options volumes. However, NSE's decision on April 4, 2025, to shift all index and stock F&O expiry to Monday impacts BSE. This places NSE's expiry a day before BSE's Sensex expiry, affecting BSE's peak activity and forcing traders to adjust. BSE's stock declined, and Goldman Sachs cut its target price. Market experts expect BSE to respond by tweaking expiry schedules, launching new products, or strengthening liquidity incentives. The dynamic nature of this competition underscores the importance of strategic agility for both exchanges in maintaining their market positions.
Wrap-up: BSE’s digital-first strategy and tech investments have significantly modernised its infrastructure, boosting competitiveness in India's evolving capital market. However, growing derivative market rivalry with NSE demands agile responses to sustain momentum and investor confidence.
Curious about how the Bombay Stock Exchange generates revenue beyond trading? This strategic breakdown of the BSE business model highlights core income streams you shouldn’t miss.
AI's rapid advancement in India's capital market offers opportunities but also challenges for regulators. While AI enhances efficiency and access, it raises issues of transparency, equity, data privacy, and algorithmic accountability.
Balancing innovation with robust regulatory oversight is crucial to harness AI benefits while mitigating risks, ensuring a secure and fair financial environment. This delicate balance will define the success of AI integration in the Indian market.
SEBI's Role and Policy Suggestions
India's main market regulator, SEBI, has taken forward-looking initiatives for algorithmic and AI-driven trading.
- Regulatory Sandbox Framework: Launched in 2019, allowing fintech startups to test new technology under SEBI's supervision.
- Consultation Paper on Algorithmic Trading: Released in 2021, addressing algorithmic trading by retail investors and seeking public input.
SEBI also recognizes the need for robust regulatory frameworks to prevent market manipulation, ensure fairness, and protect retail investors from AI risks. Despite efforts, a regulatory gap remains regarding AI risks like non-auditability, fairness, data protection, and systemic risk management. Retail platforms, while democratising investing, can lead to "cognitive overloading" and an "illusion of security" from automated recommendations, requiring standardised investor education.
To bridge gaps, cross-border trends analysis is essential, including examining EU's AI Act, UK FCA rules, and U.S. SEC policy. Research advocates practical policy suggestions for ethical and responsible AI use in India's securities market.
SEBI's Policy Suggestions for AI Use
/content-assets/e8e90bd910574ffe8141de582054684d.png)
These suggestions aim to create a comprehensive regulatory framework that supports innovation while ensuring robust investor protection and market integrity.
Financial Inclusion and Investor Protection
FinTech, including AI, has significantly expanded market access and participation, especially for new investors or those in smaller cities previously lacking formal advisory services. This has greatly facilitated financial inclusion across India.
The overarching goal is to balance innovation with integrity, protecting investor confidence, market stability, and global competitiveness. This requires a sophisticated regulatory response that leverages technology while ensuring robust investor protection and a secure, accessible financial ecosystem. This ensures that technological progress benefits all market participants equitably.
Wrap-up: Regulatory frameworks around AI in India's capital markets are evolving to balance innovation with investor protection. SEBI’s policy suggestions aim to promote ethical AI use while safeguarding transparency, fairness, and financial inclusion.
To understand how SEBI’s evolving regulatory landscape is influencing market infrastructure and trading dynamics at the BSE, dive into this in-depth BSE regulatory impact breakdown.
The future of securities trading in India is on a fast track to complete digital transformation. AI's role in the stock market is expected to expand further, making trading more efficient, transparent, and accessible.
This ongoing evolution will continue to shape how individuals and institutions engage with financial markets, ushering in a new era of digital finance.
Continuing Digital Evolution Trends
Emerging trends and technologies will continue to shape the financial industry:
- Quantum Computing: Combined with AI, could revolutionise stock trading by processing complex datasets at lightning speed for ultra-precise market predictions.
- Generative AI (GenAI) and Natural Language Interfaces: These are being developed to generate research reports, translate regulatory releases, and engage with customers through natural language, mimicking human advisors.
- Blockchain and Tokenisation: India explores blockchain for real-time, tamper-proof transactions, offering fractional ownership and smoother cross-border trading.
- e-AGMs and Digital Governance: Companies increasingly hold e-Annual General Meetings and facilitate electronic shareholder voting, enhancing participation and transparency.
- Universal KYC and Compliance Automation: India likely to adopt Universal KYC, a single digital identity for financial entities, streamlining onboarding and compliance.
These trends collectively point towards a future market that is more interconnected, efficient, and accessible, driving continuous innovation.
Wrap-up: BSE’s future lies in embracing cutting-edge technologies like AI, blockchain, and quantum computing to drive a fully digital, transparent, and inclusive market. These innovations will redefine how investors interact with India's financial ecosystem.
Here’s a great video on BSE - 150 Years: The Legacy Of Asia's Oldest Stock Exchange by ET NOW on YouTube, you should watch it. It beautifully captures the BSE’s journey and key milestones.
The Indian securities market is rapidly transforming through AI and digitalisation, bringing unprecedented efficiency and accessibility. The BSE is actively embracing this shift, implementing electronic trading and investing in advanced technologies, driven by increasing retail participation.
However, this evolution presents challenges such as market volatility, data security, and the need for greater transparency in AI-driven decisions. Regulatory bodies like SEBI are proactively addressing these with guidelines and policy suggestions. The future success of the Indian stock market, including BSE's role, hinges on balancing innovation with robust regulation, ethical governance, and investor protection. The optimal path forward lies in the collaboration between technology and human oversight, fostering a resilient and inclusive financial ecosystem.
Q1: What is driving the digitalisation of Indian stock exchanges?
Digitalisation is driven by increased retail investor participation, SEBI's regulatory pushes, demand for faster transaction speeds (e.g., T+0 settlement), and India's "Digital India" vision.
Q2: How has AI impacted investment strategies in India?
AI has revolutionised investments via robo-advisory services, advanced algorithmic trading, predictive analytics for market forecasting, sentiment analysis, and enhanced risk management and fraud detection.
Q3: What are the main benefits of AI in Indian stock trading?
Key benefits include enhanced data analysis, improved accuracy and real-time decision-making, automation through algorithmic trading, and democratisation of sophisticated trading tools.
Q4: What are the significant challenges of using AI in the Indian stock market?
Challenges include potential for increased market volatility, systemic risks from homogeneous trading, regulatory gaps, issues of non-auditability and algorithmic bias, data security, and over-reliance on AI models.
Q5: How is BSE responding to digitalisation and innovation?
BSE transitioned to electronic trading, invested in advanced data centre infrastructure (e.g., with CtrlS Datacenters), and plans further investments in AI, ML, blockchain, and autonomous databases to enhance efficiency and security.
Q6: What is SEBI's role in regulating AI in India's capital market?
SEBI established a Regulatory Sandbox and issued consultation papers on algorithmic trading. It advocates policies like mandatory AI disclosure, AI literacy certification, and explainable AI (XAI) compliance.
Q7: What is the T+1 settlement cycle, and what is the goal for the future?
T+1 settlement means transactions settle one day after trade date. India aims for T+0 (same-day settlement) and eventually instant settlement for immediate share transfer.
Q8: Why are depositories like NSDL and CDSL important in India?
NSDL and CDSL are crucial for electronic trading as they hold dematerialised shares, eliminating physical certificate risks. They enable seamless buying, selling, and real-time portfolio monitoring.